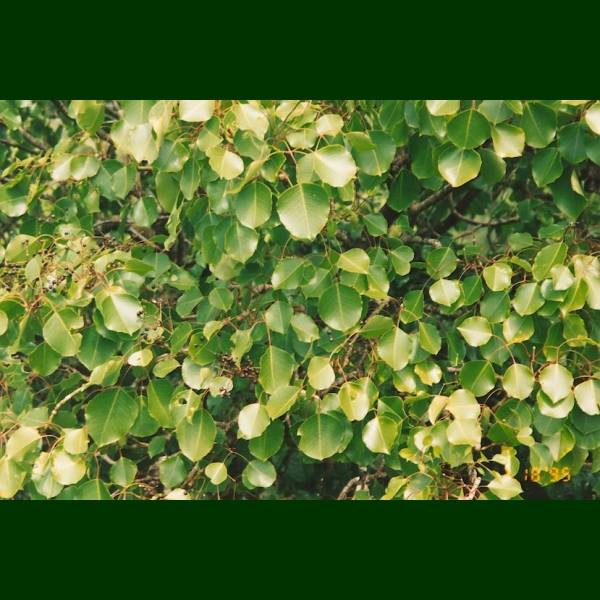
Hawaiian Name(s): ‘ōlapa, lapa, lapalapa
Hawaiian Name(s): ‘ōlapa, lapa, lapalapaScientific Name: Cheirodendron (5 species)
Vernacular Name: none
Family: Araliaceae
Status: endemic
Authority: C. dominii Kraj., C. fauriei Hochr., C. forbseii (Sherff) Lowry, C. platyphyllum (Hook. & Arn.) Seem., C. trigynum (Gaudich.) A.Heller
Description: Tree to 10 m.
Habitat Five species, occuring most often in mesic to wet forests. C. dominii, C. fauriei, and C. forbesii only on Kaua‘i (Wagner et al. 1990:225–228).
Medicines: The tap root bark is combined with root bark of ‘uhaloa (Watheria indica), root bark, flowers, fruit, and leaves of pōpolo (Solanum americanum), koa bark (Acacia koa), noni fruit (Morinda citrifolia), and kō kea (white sugarcane, Saccharum officinarum) to cure a loss for the desire to drink water (Chun 1994:230–231).
Non Medicinal Uses: Blue dye from fruit, leaves, and bark (post-contact? Abbott 1992:57; Krauss 1993:66); leaves for lei (Krauss 1993:77); wood used for bird catching spears, ka wili ‘ia i ka manu (Abbott 1992:106; Malo 1951:21); soft wood will burn when freshly cut (green) (Little and Skolmen 1989:256). In the Ethnology Collection at Bishop Museum there is a post-contact example of the wood made into a bowl.
Specific gravity of wood: unknown
Famous Locations:
Mele:
`Ōlelo Noeau:
Dye Color and Parts: Bluish-black (fruit, lvs, bark)
Kino lau:
Location on Bishop Museum Kalihi Campus:
Propagation Information: Native Plants Hawaii.
Seed: Seed length approximately 4 mm. Photograph: H.Lennstrom. Species: C. trigynum.

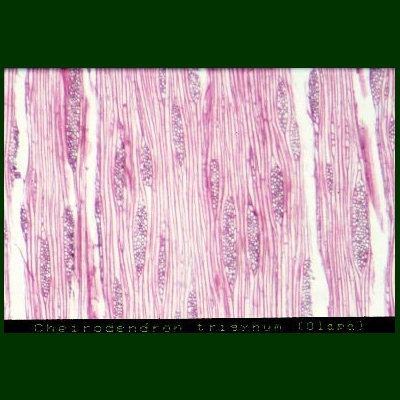
Microscopy
Cross Section: Field of view: 2.6 mm x 1.6 mm. Photograph: H.Lennstrom.
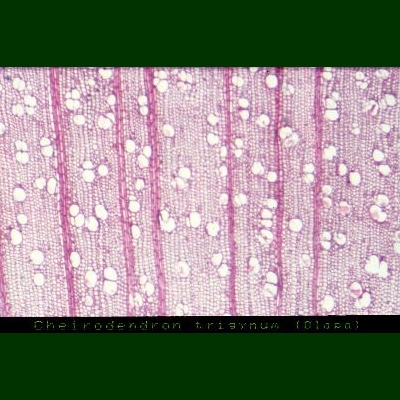
Radial Section: Field of view: 2.6 mm x 1.6 mm. Photograph: H.Lennstrom.
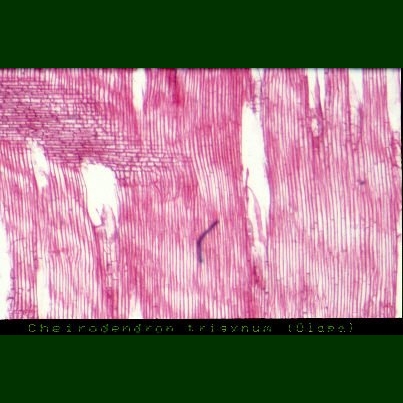
Tangential Section: Field of view: 2.6 mm x 1.6 mm. Photograph: H.Lennstrom.